Techpally Hints the Relevance of HTTP Codes in SEO
If you surf the internet regularly, and open web pages, you must have been in a situation where a page returns an error instead of loading the content of the webpage.
You surf the Internet or maybe even want to call up a very specific website – but after entering the URL in the web browser, the following error message appears
“This page cannot be found”. Plagued by frustration, people leave the site hoping to find the information they need elsewhere.
But what if a 404 error message hits your landing page, and your target visitors are not able to read your sales pitch let alone, engaging with your CTA, and converting to customers.
You can find out what HTTP status codes are, what they are and what they say in this blog post.
Also, how to Recognize status codes and improve website performanc, and Communication history between web browser and server.
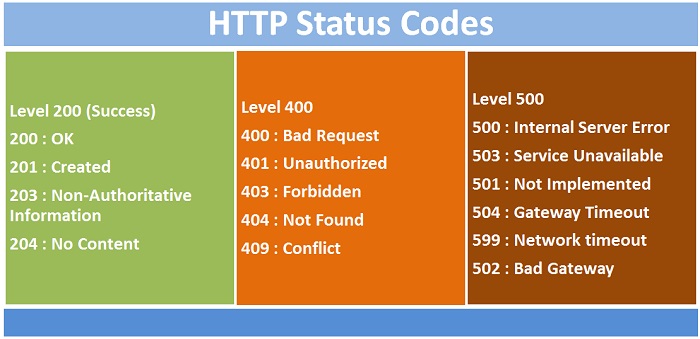
THE MOST IMPORTANT HTTP STATUS CODES AND WHAT THEY MEAN
There a lot of error codes a webpage can generate, depending on the problem, and the origin of the error, either from the server, browser or others.
There are also status codes for successful webpage processing.
According to Techpally, here are the common HTTP status or error codes you’d find on the internet.
HTTP code 200 – The request was successfull, therefore, the webpage would be processed correctly.
The page was successful and there are no other processes running in the background.
HTTP code 301 – This is an error code, and this request means the webpage does not exist on the server again.
Not only that, the webpage does not exist again and has been permanently moved.
You don’t see any special process in the browser, but in this case, a URL that no longer exists is forwarded to another page.
The website operator decides which URL is forwarded to.
HTTP code 302 – This response code means that the URL of the requested resource has been temporarily changed.
Changes to the URL may also be made here in the future. The same URL should therefore be used by the customer in future requests.
HTTP code 404 – This is the commonest of all the HTTP status codes.
For this request, the web page no longer exists and will not be redirected to another page. So the browser shows a 404 error page.
HTTP code 500 – This HTTP status code shows that there are unexpected problems on the part of the server and it’s temporary.
Of course, there are also other status codes that can be assigned to classes 2xx, 3xx and 4xx. However, these are very rare and have little meaning for SEO.
HOW CAN I IDENTIFY STATUS CODES THAT ARE NOT VISIBLE?
Unfortunately, most of HTTP status codes can not be seen from the front end, the status codes 404 which means the webpage is not found, and the status code 503, which means it’s not available can be seen by the user.
However, there are other status codes that are not obvious, says businesspally boss.
These include, for example, the status code 200 and the 301 redirect. However, so that you can still remove errors, you need browser extensions, i.e. tools to analyze the status codes.
We recommend the Techpally Trace Extension, which we use regularly in our day-to-day agency work.
Access to a page with status code 200. A webpage that no longer exists, return with a 404 status codes.
This means the access to a page that no longer exists and is being redirected to another page.
Conclusion
Not only can individual status codes be devastating for usability, SEO performance can also be negatively influenced by one or the other status code, says chaktty.
The above-mentioned important tips on how to read status codes and ultimately optimize them, not only to improve your website’s SEO performance, but to also enhance your customers viewing experience.
Customer satisfaction on your webpages also means that search engines will add more votes of confidence to your website and increase its rank.