Adobe XD Prototyping: Advanced Techniques to Design Like a PRO
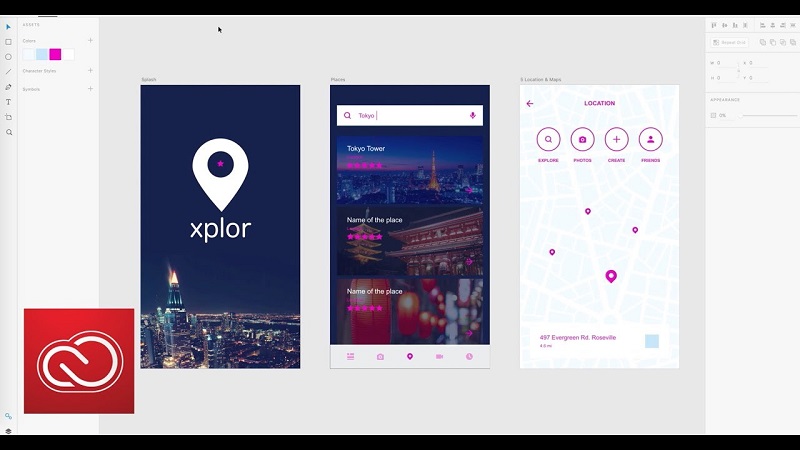
What is Adobe XD? It’s a vector editor for designing any user interface (UI-UX), from smartwatches to full-fledged websites. Nowadays, XD Design is becoming more well-known. Converting design to WordPress is rather actual today as well. Converting Adobe XD Design To WordPress makes the program more convenient for usage and saves time.
Here you will learn more about the features of Adobe XD, why it has become such a popular tool in web design, and what techniques to follow to design like a PRO.
What Does Adobe XD Do?
It’s important to remember that Adobe XD solves two major problems that neither Photoshop nor any other graphic design tool could handle:
- Interaction design is not static. A designer cannot show the dynamics of a future website using only regular pixels.
- Modern design involves more than just creating a finished, polished picture. Design, interaction, and behavior are essential steps in UI-UX design.
Adobe XD is the ideal vector editor for UI development, interactive design, prototyping, and detailed application design. It is suitable for single designers as well as for teamwork.
Adobe XD Features
Among the key features of Adobe XD are the following:
- Prototyping tools
- 3D transformation
- Animations and transitions
- Components (adaptive and customizable)
- Support for third-party plugins and add-ons
- Adaptive resizing of content
- Repeating grid
Here are some features that Adobe XD includes. I’ll name three of my favorites.
What is Adobe XD Prototyping?
Prototyping is one of the initial stages of development, during which the preliminary design of the site, banding, application or another project (its structure with a schematic representation of the main elements) is created.
During prototyping, a mockup is created to simulate user interaction with the interface of the project. Prototypes are often made interactive (clickable).
The prototype presents the project to the customer and evaluates its usability. Testing the prototype allows you to identify and eliminate mistakes before investing in developing the final design solutions and code.
The prototype can be drawn on paper or created in a graphic editor. The main difference between these methods is the elements’ level of detail and clickability.
Why Do You Make Prototypes?
The main purpose of prototyping is to save money and time. It’s challenging to create the perfect product the first time. Prototyping allows you to test the selected version of the solution without significant investments, make changes if necessary, and only proceed to design and programming.
Prototyping solves several significant problems:
- Finding the best ideas. Prototyping is done quickly, so you can prepare several variants to test hypotheses and then choose the most successful one. This is especially important for startups.
- Error detection. At the mockup stage, you can trace key flaws in your future website or app. You spend less time, money, and effort to fix them than if you had to adjust the final product.
- Usability Assessment. Developing prototypes and testing user scenarios on them is a great opportunity to check user-friendly and Responsive Website Design
Stages of prototyping
- Goal setting. It happens at a meeting of all participants interested in the project’s success. The clearer and more precisely formulated the goals, the easier it is to put forward and test hypotheses to detail the prototype.
- The aims should be as concrete as possible: to develop a selling landing page to present a new service and to think over a corporate site to increase coverage and brand awareness.
- Conducting research. To create a quality prototype, it is essential to study the client’s business, the features of his product, and the target audience.
- Formulating hypotheses. It is essential to understand exactly what you want to test with prototypes. This will help make prototyping as effective as possible.
- Considering the study results and the hypotheses formulated, a mockup of the future site or app is created.
Designing a prototype site consists of several basic steps:
- Construction of the site grid;
- Designing the home page and placing all the planned content blocks on it, including interactive ones: clickable links, sliders, pop-up forms, and drop-down lists;
- creating the remaining pages of the site.
- Focus group testing. It allows you to check how the user interface will work, whether there are gaps in logic, and to understand what changes need to be made before handing the project over to developers, layout designers, and designers. Before testing, you should agree on a prototype with the client.
- Adding new details and making changes based on testing results.
Advanced Adobe XD Prototyping Techniques to Design Like a PRO
The main feature of prototyping is that it is possible to design websites and applications without programmers and still achieve a high level of detail. Adobe XD makes it simple to prototype your concepts, from simple transitions to complex interactions. In this post, we’ll leverage Adobe XD’s more sophisticated prototype tools to build engaging, robust interactions that support your narrative.
Below are several essential techniques to help design like a Pro:
-
Establishing micro-communications
The smallest of features can significantly impact how someone uses a product or application. Understanding how an element reacts to touch or changes states can help define an application’s experiences.
-
Auto-Animate
With Auto-Animate, you can intelligently transfer and change objects across artboards or states, taking prototypes to a new level beyond straightforward transitions and dissolves. By doing so, you can produce rich transitions that seem more natural. Using Auto-Animate may make animating charts and data slick and easy while giving interactions like floating action buttons liveliness.
-
States
It’s no longer necessary to create many artboards and maintain their synchronization to provide interactions for toggle buttons, dropdown menus, and hover states. Any component can now have many states that can be linked together in prototype mode thanks to Component States in Adobe XD. As a result, a single component can have reusable states for many interactions, like hovering, clicking, making mistakes, and more.
-
Realistic scrolling
Even though it has become such a crucial aspect of online browsing and interactions with mobile devices, scrolling is a frequently forgotten behavior when prototyping experiences. It’s essential to prototype realistic scroll experiences because scrolling occurs everywhere, whether swiping through an image gallery or a social media feed. There are various ways to implement the scroll interactivity you want in Adobe XD.
-
Fixed components
The “Fix Element for Scrolling” function in Adobe XD enables items to be selected and kept in place when an artboard is scrolled, making it great for mobile device prototypes and creating fixed backdrop scrolling effects. This makes creating fixed navigational elements and floating action buttons simple and uncomplicated.
-
Anchor links
Anchor links can help you replicate the user experience if you’re designing a website with a single-page scroll format or buttons that go to different sections within a single page. Selecting the “Scroll To” action in prototype mode and dragging the prototype arrow to the group the page should scroll to are all it takes to use anchor links in Adobe XD. The scroll-to position can be adjusted precisely to the scroll position using the y-offset handle.
-
Give your prototype a voice.
The use of voice and audio in digital products is growing along with the proliferation of smart assistants and the emphasis on accessibility. Voice and audio can be used in prototypes using Adobe XD to produce lifelike experiences for voice assistant applications and to use audio to give user feedback.
Voice commands can be used as triggers for prototype activities in Adobe XD and support for Tap, Time, Drag, Keyboard, and Gamepad. This means that actions can be started with just one or a few spoken syllables.
Conclusion
Thus, prototyping allows you to simulate the functionality of a finished project, website, or application. This is necessary for testing hypotheses and identifying problem areas before the project is submitted to design and development. In this way, following several techniques, everyone can design like a PRO in Adobe XD.